



Next: References
Up: No Title
Previous: Scope for Improvement
Some sample results of the discussed algorithms from the various routines
implemented in ANSI C are shown here.
In all the BSP tree construction calculations,
MAX_CANDIDATES = 10. Also, Ni denotes the number of polygons in the
input and No denotes the number of polygons in the output.
On a 486 DX2-66 with 8 MB RAM running Linux v. 1.3.47, the
time taken was
- Mushroom (Ni = 240)
 2 sec.
(Figure
2 sec.
(Figure ![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
- Goblet (Ni = 470)
 5 sec.
(Figure
5 sec.
(Figure ![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
- Seashell (Ni = 1680)
 8 sec.
(Figure
8 sec.
(Figure ![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
- Teapot (Ni = 3751)
 42 sec.
(Figure
42 sec.
(Figure ![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
The artificial intersections due to BSP Tree construction are clearly
seen in the output of the first few examples (Figures
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) ,
,
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) ,
,
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) and
and
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) ).
).
Figure 4.1:
Input - Mushroom wire frame (Ni = 240)
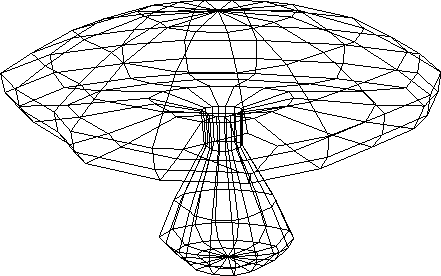 |
Figure 4.2:
Output - Mushroom rendered after BSP sorting (No = 481)
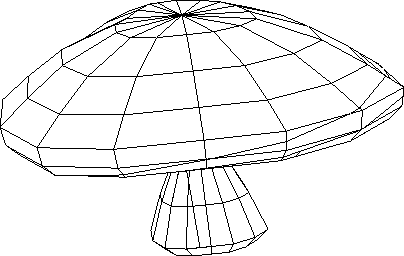 |
Figure 4.3:
Input - Goblet wire frame (Ni = 470)
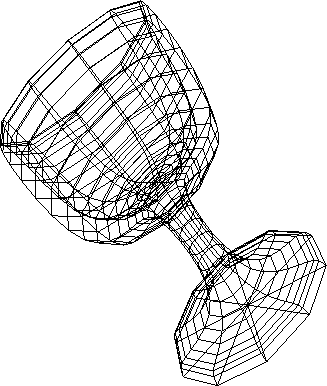 |
Figure 4.4:
Output - Goblet rendered after BSP sorting (No = 1109)
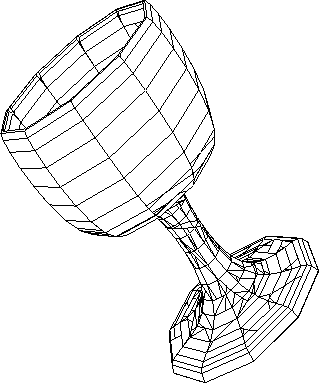 |
Figure 4.5:
Input - Seashell wire frame (Ni = 1680)
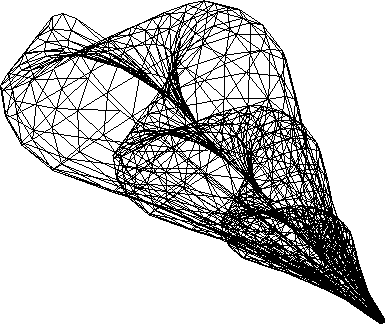 |
Figure 4.6:
Output - Seashell rendered after BSP sorting (No = 3706)
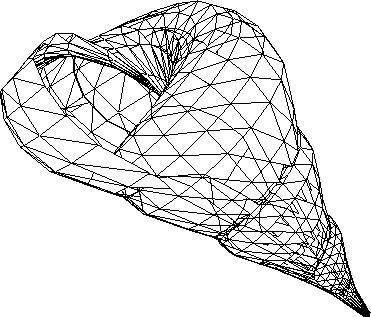 |
Figure 4.7:
Input - Teapot wire frame (Ni = 3751)
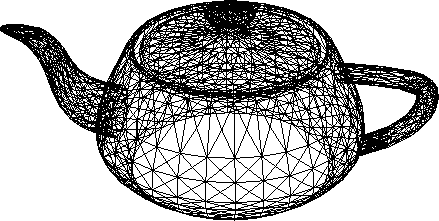 |
Figure 4.8:
Output - Teapot rendered after BSP sorting (No = 7743)
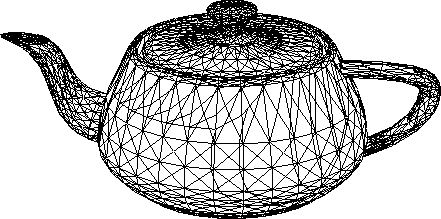 |
Figure 4.9:
Example - Input to BSP routine (Ni = 12)
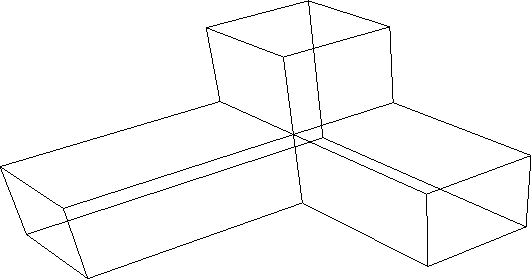 |
Figure 4.10:
Example - Output after BSP sorting (No = 12)
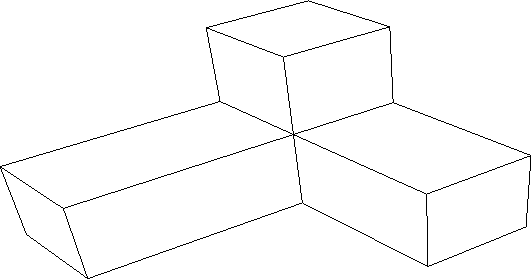 |
Figure 4.11:
Example - Input to Hidden Line Removal routine (Ni = 10)
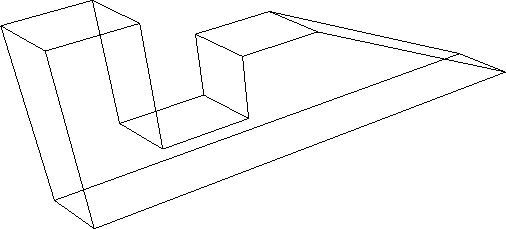 |
Figure 4.12:
Example - Output from Hidden Line Removal routine (No = 7)
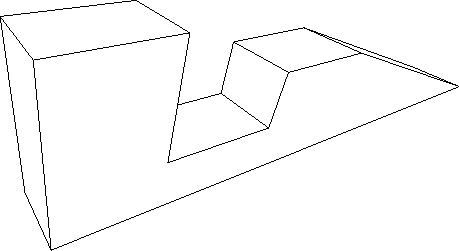 |




Next: References
Up: No Title
Previous: Scope for Improvement
Anirudh Modi
4/15/1998
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) )
)
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) ,
,
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) ,
,
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) and
and
![[*]](../../../images/cross_ref_motif.gif) ).
).