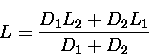Next: Delaunay Triangulation
Up: Advancing Front Triangulation
Previous: New point insertion
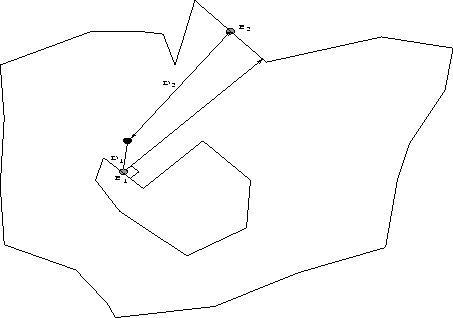
The edge of the initial front closest to the
mid-point P of the base edge is found. A normal is drawn through the
mid-point of that edge and the closest edge of the initial front that it
intersects is determined
(Figure 3.4).
Figure 3.4:
Direct graded triangulation
 |
If the distance of point P
from mid-point of both the edges is D1 and D2 respectively and if
L1 and L2 are the respective edge
lengths then the required length of the new edges is calculated as
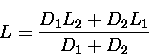
Triangulation using this method for selection of trial point is
termed as direct graded triangulation which is implemented here in
IITZeus (Figure 3.5).
This algorithm requires many calculations and hence slows down the
triangulation slightly. [Sha96]
Figure 3.5:
Advancing front triangulation - an example
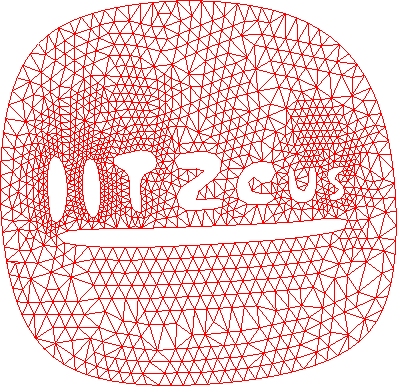 |
Anirudh Modi
1/16/1998